Early Dental Care

Cleaning and Fluoride
Your child’s teeth will be cleaned to remove plaque (bacteria) and tartar (calculus) that can cause gum disease and tooth decay. Fluoride will be applied to the teeth to make them stronger and more resistant to tooth decay. A thorough cleaning and fluoride treatment every six months has been shown to be an effective way to prevent dental disease.
Bitewing Radiographs
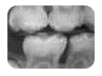
Bitewing radiographs enable us to evaluate and to diagnose possible decay in between the teeth.
Panoramic Radiograph
Panoramic radiographs provides an overall view of your child’s mouth. It reveals missing permanent teeth, extra teeth, abnormal growths, and other problems. A panoramic film is normally taken on children six to seven years of age.
Sealants
The chewing surfaces of children’s teeth are the most susceptible to cavities and least benefited by fluorides. Sealants are adhesive coatings that are applied to the tops of teeth and can be highly effective in preventing tooth decay.
Silver Fillings
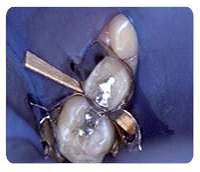
Silver fillings (amalgams) are used to restore or “fill” decayed areas in teeth. A tooth has five surfaces (the chewing surface and four sides). The decay may involve any or all of these surfaces.
Tooth Colored Fillings
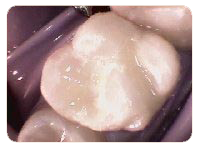
Tooth colored fillings are used to restore teeth for which cosmetic appearance is important. Tooth colored fillings (composites) are used to repair fractured teeth and/or areas of decay. The shade of the restorative material is matched as closely as possible to the color of the natural tooth. A tooth colored filling that covers the entire tooth is called a Strip Crown.
Stainless Steel Crowns
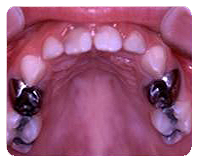
Stainless steel crowns are silver colored crowns used to restore teeth that are too badly decayed to hold fillings. Crowns with white facings can be used on front teeth.
Pulpotomy
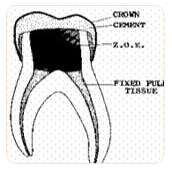
The procedure consists of treating the infected portion of the nerve to avoid extracting the tooth. A stainless steel crown is usually placed on the tooth after the pulpotomy.
Pulpectomy
A pulpectomy is necessary when the nerve (pulp) or the tooth is dead or abscessed. The entire infected pulp is removed from the roots of the tooth and medication is placed in the root canals.
Extractions
Extractions are done only as a last resort. If a baby molar is removed prematurely, a space maintainer may be used.
Space Maintainers
Space maintainers are used when a baby tooth has been prematurely lost to hold space for the permanent tooth. If space is not maintained, teeth on either side of the extraction site can drift into the space and prevent the permanent tooth from erupting.
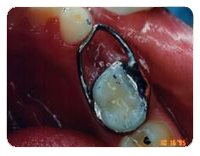
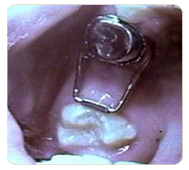
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is used to anesthetize or numb the tooth or teeth that are to be treated. This is done after a topical gel is placed on the gum with a Q-tip to numb the area before the injection is given.
Rubber Dam
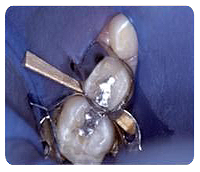 Rubber dams are used to isolate the teeth being repaired. The “rain coat” helps keep saliva out of the tooth preparations and helps protect the soft tissues of the mouth.
Rubber dams are used to isolate the teeth being repaired. The “rain coat” helps keep saliva out of the tooth preparations and helps protect the soft tissues of the mouth.
Lingual Erupting Permanent Incisors
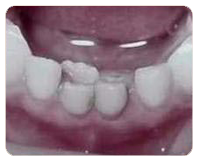
This occurs very often and can be a sign of mandibular crowding. It is not an emergency and is often resolved with no treatment. If the primary incisor is mobile, treatment is not recommended. If the primary incisor is not mobile and a radiograph reveals that the root of the primary tooth has not resorbed, the primary tooth may need to be removed. Again, this is not an emergency. The permanent tooth will always move forward as long as there is sufficient arch length.

